What is Electromyography (EMG)?
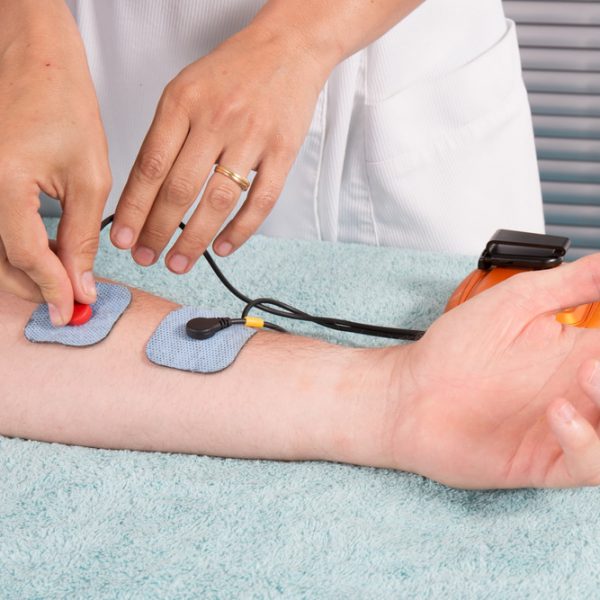
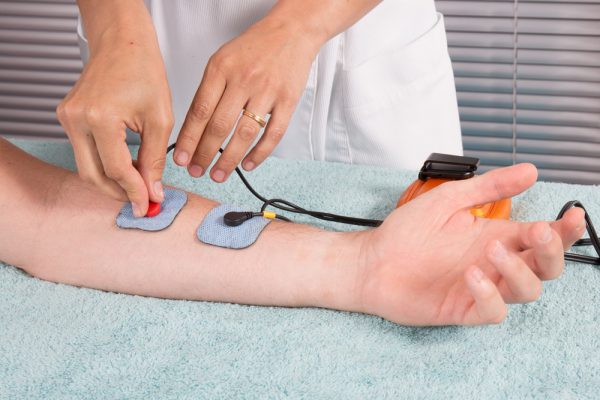
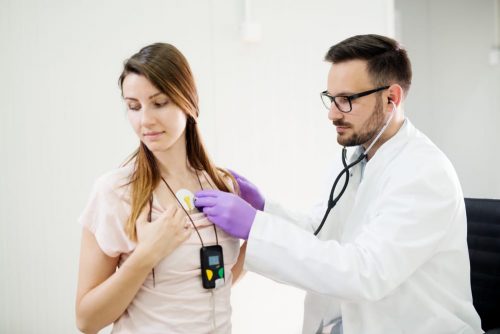
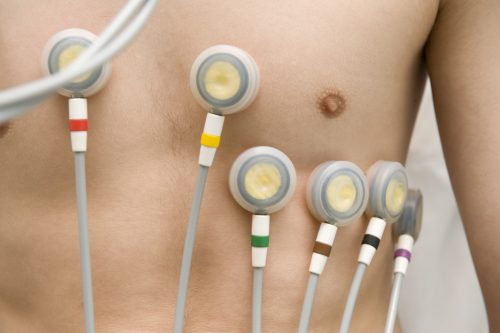
Electromyography and neurography help diagnose a number of diseases of the nervous and muscular system, monitor the situation and provide evaluation of the treatment. The procedure is performed using an instrument so called electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram.
This electromyograph can detect the electric potential which is generated by the muscle cells, in the period when these cells are neurologically or electrically activated. Provided signals are analyzed to detect the medical abnormalities and also to analyze the biomechanics of the person.
EMG test
The EMG tests provide information about the injured neurons, nerve damage and muscle disorders leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, heat, pain or weakness (flakiness) and muscle cramps.
Which diseases can be diagnosed with EMG method?
- Multifocal motor neuropathy
- Discus hernia
- Diabetic neuropathies
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myasthenia gravis
- Muscular dystrophy
- Endocrine infection/disorders
- Sensory neuropathy
- Spinal muscular dystrophy
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Infections
- Radiations etc.
What should you know before taking an EMG test?
Before taking an EMG test, there are no prior special arrangements, it’s only recommended that the patient’s skin is clean from any lotion or cream to avoid application of the EMG device. Before electromyography there were clinical neurological examinations. Today, EMG test consists of two parts:
- The first part is called neurography, which examines the speed of the conducting nerves;
- The second part is called electromyography whereby using a needle electrode is determining the electrical activity of muscles.
What results do the EMG tests provide?
EMG enables us to explain the weakness of the muscles that occurred due to disruption of the work of the nerves or muscles and shows us:
- The extent of damage to the motor nerve
- Place/location of the damaged nerve
- The segment amount of where the damage has occurred
- With constant controls, it shows whether the impairment is improving or worsens in the treatment of primary disease.